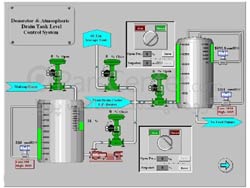
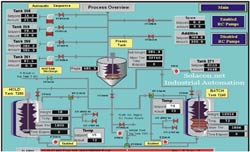
Industrial automation refers to the use of computers instead of human operators to control industrial devices and processes. Automation is a step beyond mechanization. Mechanizing means providing human servants with tools and devices that help them do their jobs. The most well-known and prominent part of industrial automation is industrial robots.
Today, applying industrial automation and precision tools in industrial processes is widespread. Process control and complex measurement systems used in industries such as oil, gas, petrochemicals, chemical industries, food industries, automotive industries, etc. require very precise and sensitive tools. Recent technological advances in process control and measurement of various industrial parameters such as pressure, temperature, flow, etc. have increased product quality and reduced production costs.
Now a days, the improvement of the quality level of products in different industries and, in addition, the quantitative increase of production, is the main objective of each industrial unit, and industrial managers have been aware of this and have focused their efforts on this goal. The need to increase the quality and quantity of a product is to use advanced and automatic machines. Machines that most of their working stages are automated and less reliant on human factors. Such machines for their proper operation require an automated command section, which is usually used by a programmable control system (for example, a programmable logical PLC). The programmable control section is programmed according to the machine's algorithm and can control the operator's functions in accordance with the instantaneous conditions and ultimately control the machine.
Keywords: Industrial automation - Computers instead of operators - Industrial control devices and processes - Beyond mechanization - Industrial robots - Process control and measurement systems - Increased product quality - Production costs reduction